How to File GST Return
This guide breaks down GST return filing in a simple, clear way for Indian businesses. Learn how to file GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, GSTR-9, CMP-08, GSTR-4, IFF, and QRMP returns. Understand due dates, ITC rules, late fees, common errors, and practical compliance steps.
A Complete GST Return Filing Step-by-Step Guide for 2026
Filing a GST return step-by-step is a messy process, but with the GST filing process mentioned below, return filing will be easier for business owners. This really means that you only need to know three things: which GST return to file online, when to file it, and how to avoid GST notices.
Before starting return filing, you only need to know three things:
- Which GST return applies to your business?
- When to file it.
- How to avoid notices.
Let’s get started with understanding how to file a GST return online step by step.
GST Filing Process & Step-by-Step Guide
Below are the step-by-step filing guides for every major GST return.
How to file GSTR-
How to File GSTR-1 (Sales Return)
This is the return where you report every B2B invoice, B2C large invoice, export, and credit/debit note.
Step-by-step process of filing GSTR-1:
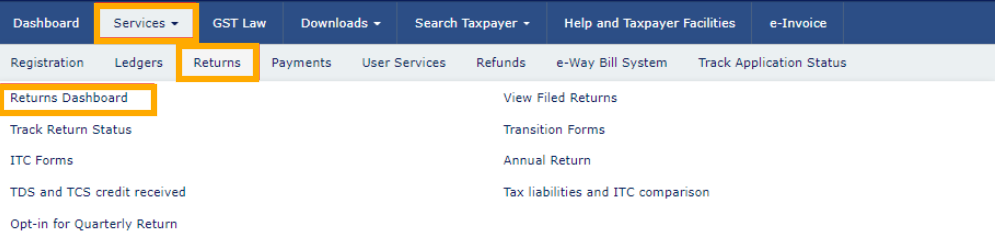
- Go to gst.gov.in and log in.
- Click Returns Dashboard.
- Select the Month/Quarter.
- Open Prepare Online under GSTR-1.
Add invoices under sections:
- B2B
- B2C Large
- B2C Small
- Exports
- CDN (Credit/Debit Notes)
- Save each section.
- Validate summary.
- Submit and file with DSC/EVC.
Tips to Fix GSTR-1 errors
Most GSTR-1 mistakes come from rushed data entry or mismatched invoices. The good news is you can fix almost all of them in the next month’s return.
Common GSTR-1 errors and fixes:
- Wrong invoice value
Amend the invoice in the B2B/B2C amendment section of next month’s GSTR-1. - Incorrect GSTIN of customer
Delete the wrong invoice and upload the correct one in the next period. - Wrong tax rate applied
Update the invoice through amendments and adjust the difference in GSTR-3B. - Missed invoices
Add the missed invoices in the next GSTR-1 as “amended/additional invoices”. - Duplicated invoices
Use the amendment section to reduce the duplicated amount.
Imp GSTR-1 Tip-
If you use e-invoicing, your invoices auto-populate, which reduces errors and speeds up filing.
How to File GSTR-3B (Tax Payment Return)
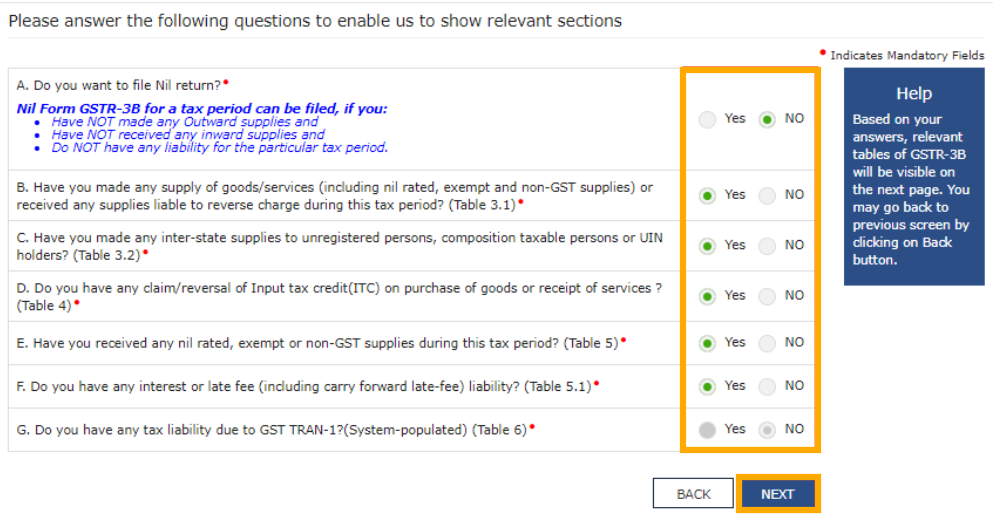
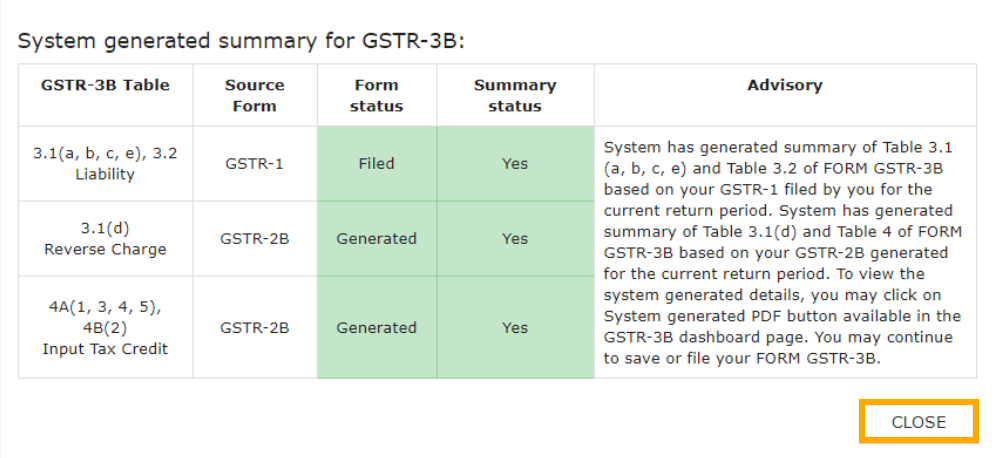
GSTR-3B is where you actually pay your tax. It’s a summary return, so stay careful.
Steps To file GSTR-3B online:
- Log in > Returns Dashboard.
- Select GSTR-3B.
- Fill outward supplies (sales).
- Fill inward supplies (eligible ITC).
- Review auto-populated data from GSTR-1.
- Check tax liability.
- Offset using ITC or cash.
- File with DSC/EVC.
Important GSTR-3B Tip-
If your ITC is insufficient, you can pay the balance through the cash ledger.
How to File a NIL Return (Fastest Method)
If there are zero transactions:
- Log in
- Returns Dashboard
- Select NIL filing option
- File GSTR-1 or 3B directly
- Confirm through OTP
Takes less than a minute and keeps you compliant.
How to File GSTR-9 (Annual Return)
This is a yearly summary of your entire financial year.
Steps to file GSTR-9:
• Log in → Returns Dashboard
• Select FY → GSTR-9
• Download system-computed summary (optional)
• Fill auto-populated tables for sales, purchases, ITC, demands, refunds
• Validate each table carefully
• Proceed to file using DSC/EVC
GSTR-9 filing Tip:
Once filed, GSTR-9 cannot be revised. Double-check numbers before submitting.
How to File GSTR-9C (Reconciliation Statement)
This return applies only if your turnover crosses the prescribed limit.
Steps to file GSTR-9:
• Download your GSTR-9C offline tool
• Fill Part A (reconciliation of turnover, ITC, tax paid vs computed)
• Fill Part B (self-certification)
• Upload JSON to the GST portal
• File using DSC
How to File GSTR-9C (Reconciliation Statement)
This return applies only if your turnover crosses the prescribed limit.
Steps:
• Download your GSTR-9C offline tool
• Fill Part A (reconciliation of turnover, ITC, tax paid vs computed)
• Fill Part B (self-certification)
• Upload JSON to the GST portal
• File using DSC
Tip for filing GSTR 9-C:
GSTR-9C is a reconciliation between GST returns and financial statements, so match figures carefully.
How to File CMP-08 (Composition Quarterly Return)
This is a simple quarterly payment form.
Steps to file CMP-08-
• Log in → Returns Dashboard
• Pick CMP-08
• Enter turnover for the quarter
• System auto-calculates tax
• Pay liability
• File with DSC/EVC
Note:
CMP-08 has no late fee, only interest if paid late.
How to File GSTR-4 (for Composition Annual Return)
Composition taxpayers file only this annual return.
Step-by-step guide to file GSTR-4:
• Login to Portal, go to Returns Dashboard, then click on GSTR-4
• Enter turnover.
• Declare inward supplies attracting reverse charge.
• Verify tax paid through CMP-08.
• File with DSC/EVC.
Quick tip GSTR-4:
Late fee applies only for GSTR-4, not CMP-08.
How to File GSTR-5 (Non-Resident Taxable Person Return)
It applies only to foreign taxpayers supplying in India.
Steps:
• Log in → GSTR-5
• Provide invoice-wise details of supplies
• Enter input tax and tax payable
• Pay liability
• File return
Filing GSTR-5 tip:
This return must be filed even if the registration period is short.
How to File GSTR-6 (Input Service Distributor Return)
GSTR-6 is filed for ISDs (e.g., head office distributing ITC to branches).
Step-by-step guide to file GSTR-6:
• Log in → GSTR-6
• Review auto-populated invoices from suppliers
• Accept/modify invoices
• Add credit distribution details
• File with DSC/EVC
Tip for filing GSTR-6:
Accuracy is crucial because wrong ITC distribution affects branch-level ledgers.
How to File GSTR-7 (TDS Return)
GSTR-7 is filed by government departments or notified bodies that deduct TDS.
Steps:
• Log in → GSTR-7
• Enter TDS deducted, GSTIN of deductee, and payment details
• Verify liability
• File with DSC/EVC
File GSTR-7 easily:
The deductee gets TDS credit only after this return is filed.
How to File GSTR-8 (TCS Return by E-commerce Operators)
Filed by platforms like Amazon, Flipkart, etc.Steps:
• Log in → Returns Dashboard
• Select GSTR-8
• Enter supplies made through the platform
• Declare TCS collected
• Pay tax → File
GSTR-8 Filing Tip:
Sellers can claim TCS only after GSTR-8 is filed.How to File QRMP Scheme Return
(Quarterly GSTR-3B + GSTR-1)
GSTR-3B Quarterly Filing Steps:
• Log in → Returns Dashboard
• Select GSTR-3B (quarterly)
• Enter outward supplies
• Enter ITC
• Pay tax → File
• Due date is 22nd/24th depending on state
GSTR-1 Quarterly Filing Steps:
• Log in → Returns Dashboard
• Select GSTR-1 (quarter)
• Add all invoices
• File by 13th after quarter ends.
How to File IFF (Invoice Furnishing Facility)
Used only in QRMP scheme to upload B2B invoices in Month 1 and Month 2.
Steps:
• Log in to Returns Dashboard.
• Select the filing month.
• Add B2B invoices.
• Click on Save, then Submit, then finally click on File.
• Window: 1st to 13th of Month 1 and Month 2 only
Quick Tip for Filing IFF:
With IFF, buyers are able to claim ITC earlier.
Checklist: Things to do Before Filing GST Return (Don’t Skip This)
Most GST filing issues come from missing data or mismatches. A 3-minute check saves hours of correction.
- Reconcile sales with GSTR-2B and e-way bills
- Check if ITC is eligible (reverse ineligible amounts)
- Verify B2B invoices, HSN codes, place of supply
- Keep debit and credit notes ready
- Check if previous periods are filed
- Ensure you have enough cash balance or admissible ITC
- Once this is clear, you won’t face “mismatch” errors later.
Types of GST Returns Guide
Monthly and Quarterly returns
| Return Type | Who Files It | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| GSTR-1 | Regular taxpayers | Report outward supplies (sales), exports, credit/debit notes |
| GSTR-3B | Regular taxpayers | Summary return to pay tax after ITC adjustment |
| IFF (Invoice Furnishing Facility) | QRMP scheme taxpayers | Upload B2B invoices for Month 1 and Month 2 of the quarter |
Annual Returns
| Return Type | Who Files It | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| GSTR-9 | Regular taxpayers | Annual summary of sales, purchases, ITC, liabilities |
| GSTR-9C | Taxpayers with turnover above the notified limit | Self-certified reconciliation of books vs GST returns |
Special Returns
| Return Type | Who Files It | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| GSTR-4 | Composition taxpayers | Annual return containing turnover and tax details |
| CMP-08 | Composition taxpayers | Quarterly tax payment and simple statement |
| GSTR-5 | Non-resident taxable persons | Return for supplies made in India |
| GSTR-6 | ISD (Input Service Distributor) | Distribute input tax credit to branches or units |
| GSTR-7 | TDS deductors | Return to report TDS deducted under GST |
| GSTR-8 | E-commerce operators | Report TCS collected and supplies made through the platform |
Read more: More on GST return, and types of GST returns.
GST Return Filing Due Dates (2025 GST Calendar)
The following is based on return type vs. who must file vs. frequency of GST return filing online.
A. Regular Taxpayers – Monthly GST Return Due Dates
| Return Type | Filing Frequency | Due Date |
|---|---|---|
| GSTR-1 | Monthly | 11th of next month |
| GSTR-3B | Monthly | 20th, 22nd, or 24th (state-wise staggered) |
B. QRMP Scheme Taxpayers – Quarterly GST Return Due Dates
| Return Type | Frequency | Due Date |
|---|---|---|
| IFF (Invoice Furnishing Facility) | Monthly (Month 1 and Month 2 of the quarter) | 1st–13th of Month 1 and Month 2 |
| GSTR-1 | Quarterly | 13th of the month after the quarter ends |
| GSTR-3B | Quarterly | 22nd or 24th of next month after the quarter (state-wise groups) |
For QRMP taxpayers, quarterly GSTR-1 is due on the 13th of the month after the quarter, and quarterly GSTR-3B is due on 22nd /24th, depending on the state category.
C. Composition Taxpayers – GST Return Due Dates
| Return Type | Frequency | Due Date |
|---|---|---|
| CMP-08 | Quarterly | 18th of the month after the quarter |
| GSTR-4 | Annual | 30 April of the next financial year |
State-wise Groups for GST Quarterly Return Deadlines
| Group | States / Union Territories | Quarterly Return Due Date |
|---|---|---|
| Group A (22nd) | Chhattisgarh; Madhya Pradesh; Gujarat; Maharashtra; Karnataka; Goa; Kerala; Tamil Nadu; Telangana; Andhra Pradesh; Puducherry; Daman & Diu; Dadra & Nagar Haveli; Andaman & Nicobar Islands; Lakshadweep | 22nd of month following quarter |
| Group B (24th) | Himachal Pradesh; Punjab; Uttarakhand; Haryana; Rajasthan; Uttar Pradesh; Bihar; Sikkim; Arunachal Pradesh; Nagaland; Manipur; Mizoram; Tripura; Meghalaya; Assam; West Bengal; Jharkhand; Odisha; Jammu & Kashmir; Ladakh; Chandigarh; Delhi | 24th of month following quarter |
Also read:
Monthly GST deadlines 2025, 2026-2027.
GST Payment deadlines
Solutions to GST Return Filing Problems
a) What if previous months are not filed?
You must file old periods first. The GST portal won’t allow you to file the current month otherwise.
b) What if ITC is less than the tax payable?
You still pay tax through a cash ledger.
c) Filing after cancellation revocation
Once GSTIN is active again, file all pending periods in order.
d) Credit note issued after filing GSTR-1
You can report it in the next month’s GSTR-1.
e) Cash ledger has balance, but return isn’t filed
Payment is not considered done until you file GSTR-3B.
How to Avoid GST Notices
Follow these tips to avoid GST notices:
- Don’t claim ITC beyond GSTR-2B.
- Report correct HSN for each item.
- Don’t mismatch invoice numbers.
- Avoid filing NIL GSTR-1 when you actually have sales.
- Reconcile every month to avoid scrutiny under Section 73/74
- These are tiny details but extremely important for accuracy.
Read more: last date for gst payment
GST Late Fees and Interest Structure Explained
| Scenario | Amount | Delay | Rate | Formula | Interest Payable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tax paid late | ₹10,000 | 10 days | 18% | 10,000 × 18% × 10/365 | ₹49 |
| Excess ITC claimed and used | ₹5,000 | 20 days | 24% | 5,000 × 24% × 20/365 | ₹66 |
Example 1: Tax paid late at 18%
You had to pay 10,000 GST, but you paid 10 days late.
Interest = 10,000 × 18% × (10/365)= ₹49.31
Rounded off, ₹49.
Example 2: Excess ITC claimed at 24%
You wrongly claimed 5,000 ITC and used it. You correct it after 20 days.
Interest = 5,000 × 24% × (20/365)
= ₹65.75
Rounded off, ₹66.
GST Interest Calculation Table
| Particulars | Interest Rate | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tax paid late | 18% per annum | Tax × 18% × Days/365 | 10,000 paid 10 days late → ₹49 |
| Excess ITC claimed | 24% per annum | ITC × 24% × Days/365 | 5,000 reversed after 20 days → ₹66 |
| Short-paid tax | 18% per annum | Difference × 18% × Days/365 | 2,000 short for 15 days → ₹15 |
| Wrong ITC utilisation | 24% per annum | ITC × 24% × Days/365 | 8,000 wrong ITC for 30 days → ₹158 |
Late Fee for (GSTR-3B & GSTR-1)
- Late Fee (GSTR-3B & GSTR-1)
Rs. 25 CGST + Rs. 25 SGST per day - Capped at Rs. 5,000 per return
- NIL returns: Rs. 10 + Rs. 10 per day
- CMP-08 & GSTR-4
Late fee applies only for GSTR-4 (annual), not CMP-08.
Should You Use Software for GST Return Filing?
If your invoices are high-volume or you file for multiple GSTINs, using GST software helps. Apps like GimBooks automate invoice entries, auto-fill GSTR-1/3B fields, and reduce mismatch errors. This saves time, reduces the cost of manual management, and eliminates manual errors.
Advice on Filing GST Return Guide
Filing GST returns becomes easy once you stick to a routine: reconcile data, prepare GSTR-1, file GSTR-3B, and double-check ITC. Whether you’re a small business, freelancer, retailer, or e-commerce seller, the process stays the same. And if you use GST-compliant software for small businesses, then you can easily avoid GST notices and late interest fees.
Frequently asked Questions- GST filing & common issues
Why do GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B mismatches happen?
- Supplier filed GSTR-1 after the month closed (appears in 2A, not 2B).
- Supplier uploaded to the wrong GSTIN or used the wrong period.
- Credit notes or amendments not yet reflected.
How can I claim ITC safely?
- Match purchase invoices with GSTR-2B.
- Confirm supplier filed GSTR-1 and paid tax.
- Verify GSTIN, HSN, invoice value and tax rate.
- Retain e-way bills and payment proof for large claims.
- Don’t claim ITC on blocked categories (e.g., personal use).
What happens if I enter the wrong HSN?
- If tax rate changes, you may owe extra tax + interest.
- If it’s only a classification mismatch, amend in the next GSTR-1.
- Repeated errors can invite departmental checks.
When does late fee apply vs when it doesn’t?
- Late: GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, GSTR-4, GSTR-5, GSTR-7, GSTR-8, CMP-08 (where applicable).
- No late fee if you file within the due date or when a government-wide waiver is announced.
- NIL returns may have lower daily fees (check current caps).
Can I file GSTR-3B without filing GSTR-1?
How to file GST return if the previous month is pending?
- File oldest pending return first (GSTR-1 or GSTR-3B as applicable).
- Resolve any mismatches or tax shortfalls (pay interest if required).
- Once backlog is cleared, later periods will unlock for filing.
How to revise a GST return?
- Amend the original invoice in the next month’s GSTR-1 (use amendment section).
- Adjust tax differences in the next GSTR-3B and pay interest if due.
