Process digitisation is no longer restricted to private businesses. For the industry, the government is also progressively automating its operations. The E-way bill is one example of the government's efforts to assist businesses with transportation. You must be wondering how and what an E-waybill is. To explain, you cannot just transport products from one location to another, or even outside a state's borders, without first obtaining a permit. To transfer your goods, you must first obtain official authorisation. The E-Waybill is the name of the permit. Our experts will describe how to create e waybill in the GST portal in this article. So, keep reading.
Finally, the GST council has ordered the deployment of the E Way Bill for Interstate logistics of products in all states from April 1, 2018.
But, what is GST E-Way Bill?
The Electronic Way Bill (E-Way Bill) is a one-of-a-kind bill/document created electronically for goods’ specific movement/consignment from one location to another. This movement is either interstate or intrastate and has a value of more than INR 50,000, as required by the present GST regime.
After the e-Way Bill is generated, the transporter, supplier, and recipient are given a single e-Way Bill Number (EBN). It is produced electronically using the GSTN's E-way bill site. A unique E-way Bill Number (EBN) is assigned to each e-way bill and is available to the provider, receiver, and carrier. Additionally, E-waybills may be created or cancelled by SMS, Android App, and API site-to-site connectivity.
Originally, E-way bills were a component of the VAT system, and they were created using the Delivery Note. This conveyance letter was sent along with the items, proving that the commodities being delivered had been updated on the system ahead of time to save money.
This procedure was formerly manual, requiring the collection of Delivery Notes from the VAT office and the subsequent submission of a usage proclamation. However, in the case of an E-way, the method is slightly different; it is not entirely manual and is 95 per cent digital.
An E-Way Bill is divided into two sections:
Part 1: GSTIN (supplier and receiver), invoice number, delivery address, HSN codes, and other invoice information may be found in this section.
Part 2: This section covers details about the transporter, such as the transporter ID and vehicle number.
There are different type of transporters, such as-
GST registered Transporters: In this category, the transporter gets registered in the GST Common portal and obtains a GSTIN number.
Enrolled transporters: They are small transporters who want to do transport business without registration in GST Common portal. So, the transporter needs to enrol himself in the e-waybill portal via PAN and obtain a TRANSIN that looks similar to a GSTIN number. They are called as Enrolled transporters.
Common enrolled transporters: They are GST registered transporters having multiple GSTINs for different states. This involves transhipments and updating of transporter Id of the respective state for the e-waybills.
Whether you want to convey one consignment or numerous consignments in single transportation, the site includes single and consolidated choices under EWB-01 and EWB-02. E-Waybill will be used by both the supplier and the receiver to determine the status of goods-in-transit.
Table Of Contents
- List of states where an e-way bill is applicable
- List of union territories where an e-way bill is applicable
- How to create an e-way bill instantly?
- What documents are required to create an e-way bill?
- GST e-way bill validity
- Acceptance of GST e-way bill
- Cancellation of GST e-way bill
Gimbooks is a cloud-based bookkeeping and accounting platform aimed at small and micro-sized businesses that help them create and manage documents (such as GST compliant invoices, waybills, quotations, purchase orders, delivery challans, and so on). It also helps businesses keep track of day-to-day inventory and expenses, manage various business reports, and send payment reminders to customers via mobile and web. GimBooks' major goal is to make business easier for millions of people by delivering a mobile-first, simple-to-use, and inexpensive solution.
List Of States Where An E-Way Bill Is Applicable
List Of Union Territories Where An E-Way Bill Is Applicable
- Andaman & Nicobar
- Chandigarh
- Dadar & Nagar Haveli
- Daman & Diu
- Lakshadweep
How to Create An E-Way Bill Instantly?
Any of the following procedures can be used to create the EWB-01 E Way Bill:
Web Portal for ewaybill login
1. You must enter the portal system using the username and password you generated during registration.
2. Select the’ Generate New’ option under the 'e-waybill' drop-down menu on the left side.
3. This is the most time-consuming part of the procedure. Please double-check all of the information before continuing.
- Transaction Type: If you are the recipient of the items, choose 'Inward.' The consignment's provider should choose 'Outward.'
- Sub-type: Depending on whether you picked 'Inward' or 'Outward,' you should select the appropriate sub-type from the alternatives provided.
- Document type: The available options are Invoice, Bill, Challan, Credit Note, Bill of Entry, or Others.
- Enter the invoice or document number.
- Give the invoice or other document's due date. The present date should be used, and the user should avoid entering a future date since this will result in an incorrect input.
- In the From and To sections, enter the supplier's name, address, GSTIN information, and receiver. Note: In the GSTIN field, an unregistered supplier should write 'URP' (Unregistered Person).
- Enter the consignment information in this section under the appropriate fields, including Description, HSN Code, Quantity, Unit, Value/taxable value, Tax rates of CGST and SGST or IGST (in %), and a Tax rate of Cess, if any charged (in %). Note: The matching entries of the information supplied here can be auto-populated in the GST site while completing the linked GST return after adopting the E-Way Bill.
- Enter your mode of transportation and the distance you expect to travel. While these facts are required, the two choices can be used to fill in extra information. Note: Please update the 'My masters' part of the login dashboard first for regularly used items, clients, suppliers, and transporters.
- Name of the transporter, transporter ID, transporter Doc. No., and Date
- The number of vehicles that were utilised to convey the goods.
4. Select 'Submit' from the drop-down menu. After checking data, the system either creates an e-way bill with a unique 12-digit number for your EWB-01 form or warns you of any mistakes in the data (if any).
Creating an e-way bill on the online gateway is now complete. You may change the vehicle number on an existing EWB and cancel an EWB produced. Print a paper copy and have it with you at all times. You may also print the e-way bill at any time by selecting 'Print EWB' from the 'e-Waybill' section.
Via SMS
The SMS technique can be used by entities that just want to create one bill and/or users who can't access the website. It's also a good option when you need to get something done quickly. To use this function, you must first sign up for the SMS service on the internet site.
- Enter your login credentials into the online portal. Select 'Registration' from the left-hand menu and select the SMS option from the drop-down menu.
- Please note that you must have already registered your cell number with the portal to use the SMS feature. Your registered mobile phone number has been made partially accessible. Click 'Send OTP,' enter the OTP you received through SMS, and click Verify.
For each registered GST user, you may only add up to two mobile numbers. If the same mobile number is linked to numerous user IDs, pick the mobile number that was used to generate multiple user IDs, then choose the appropriate ID and hit 'Submit.'
You are now allowed to use the SMS service. For proper usage of the SMS capability, a set of pre-defined codes must be utilised.
Through e-Invoicing
Existing users of the digital portal can log in to the e-Invoice portal using the same credentials. You may produce an e-way bill on this site using your unique IRN (Invoice Reference Number). For firms that do a large number of transactions every day, there is also the option of generating bulk e-way bills.
- Start by entering the invoice information into the e-Invoice site.
- The GSTN will assign you a unique IRN (Invoice Reference Number) and an extra QR code on the invoice after successfully verifying and validating the information. The data is subsequently uploaded to the e-way bill site in the backend, and the APIs are utilised to produce e-way bills from IRN.
- You may now produce a bill by logging onto the e-way bill site and entering the IRN.
As of 6 November, 2023, NIC has introducing 2- Factor Authentication for logging in to e-Way Bill/e-Invoice system. Now, you will receive OTP for login authentication .
There are 3 different ways of receiving this OTP. You may enter any 1 out of the 3 OTP to login. These 3 ways are-
1. SMS: OTP will be sent to your registered mobile number as SMS.
2. On ‘Sandes’ app: Sandes is a messaging app provided by government. You may download and install the Sandes app on your registered mobile number to receive the OTP.
3. Using ‘NIC-GST-Shield’ app: ‘NIC-GST-Shield’ mobile app helps you to generate OTP by using the app. This app can be downloaded only from the e-Waybill / e-Invoice portal from the link in the following steps-
-Go to ‘Main Menu->2-Factor Authentication.
-Install NIC-GST-Shield.
-Download, install and register this app on your registered mobile number.
-You will find that the time being displayed on the screen is synchronized with the e-Waybill / e-Invoice system.
-On opening the app, OTP will be displayed.
-You may enter this OTP to continue the authentication. It gets refreshed after every 30 seconds.
4. Registration for 2-Factor Authentication: On logging to e-Waybill System go to Main Menu-> 2 Factor Authentication and confirm the registration. Your OTP authentication is based on your user account, you can not use anyone else's OTP for this purpose.
The sub users of GSTIN will have separate authentication depending on their registered mobile number in the e-Way Bill/ e- Invoice System.
Creating sub-users: For improving efficiency of e-waybills, main users will create sub-users and update the registered mobile number of the sub-user. The sub-user may be granted permissions to generate e-waybill or cancel e-waybill or all the options. Further, the activities of the sub-users may be monitored by the main-user regularly.
Before we proceed further, let's take look at the necessary documents required for creating an E-Waybill.
What Documents Are Required To Create An E-Way Bill?
The sections walk you through creating a GST E Way Bill on the EWB site. Before creating an e-way bill, there are a few requirements that must be completed (including all the methods)
- The EWB site requires registration.
- The invoice, bill, or challan for the goods consignment must be present.
- If you're travelling by car, you'll need the Transporter ID or the Vehicle number.
- Transport document number and date on the paperwork if travelling by train, air, or ship.
GST E-Way Bill Validity
The CBIC has issued a notification under the Central Goods and Services Tax Rules (Fourteenth Amendment), 2020, to change the validity of e-way bills to one day for every 200 kilometres. On December 22, 2020, the CBIC issued notification No. 94/2020-Central Tax, which modifies Rule 138 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Rules, 2017. The following are how a new amendment will take effect on January 1, 2021:
- According to the revision, the e-way bill will be valid if applied to one day for every 200 kilometres travelled rather than 100 kilometres as previously. This only applies to when the ship is used for transportation, such as over-dimensional goods or multimodal shipments.
- The e-way bill was good for one day for up to 200 kilometres of travel for every 200 kilometres, and then one more day was allowed. In the case of over-dimensional goods or multimodal shipments involving at least one leg of ship transport, the e-way bill's validity is limited to one day for a distance of 20 kilometres. If you go more than 20 kilometres, you will be rewarded with one additional day.
Small firms who carry items within a 50-kilometre radius of each other in the same state have been relieved of the necessity to furnish transport vehicle information. This restriction was formerly set at 10 kilometres.
The conveyance in charge will be required to maintain the invoice, bill of supply, or delivery challan and a copy of the e-way bill or the e-way bill number in physical or Radio Frequency Identification Device (RFID) format attached to the conveyance. The tax commissioner or an authorised official can demand the e-way bill or the related number to verify the specifics of all inter-state and intra-state goods and commodity movement.
Acceptance Of GST E-way Bill
In the following situations, the produced e-way bill is accepted:
- The recipient enrolled on the common site accepts the consignment of available e-way bills.
- If the receiver does not reply within 72 hours to the provided E-way bill data, the e-way bill is deemed received by the recipient.
In the following cases, the E-way bill does not require agreement and is deemed accepted:
- The goods transit is covered by Rule 138's Annexure (14).
- When the means of transportation is non-motorized.
- If the items are moved from the airport, air cargo complex, and port to an inland container port or a freight station for customs clearance.
- If the goods are transported to the relevant regions of the states specified by clause (d) of sub-rule (14) of GST rule 138.
E-way The following situations do not need the use of a bill:
- Non-motorized transportation is used.
- Goods are transferred to the Inland Container Depot (ICD) or Container Freight Station (CFS) for Customs clearance from a Customs port, airport, air cargo complex, or land customs station.
- Goods that are supervised by Customs or are sealed by Customs.
- Goods that are carried under a Customs Bond from an ICD to a Customs port or from one customs station to another.
- Cargo moved to or from Nepal or Bhutan in transit.
- Movement of products induced by a defence organisation acting as a consignor or consignee for the Ministry of Defense.
- Empty cargo containers are being carried.
- Consignor conveying products 20 kilometres between his or her place of business and a weighbridge for weighing, accompanied by a Delivery challan.
- The Central Government, State Governments, or municipal bodies are the consignors of commodities being transported by rail.
- Goods listed in the various State/Union territory GST Rules as exempt from E-Way bill requirements.
- Transportation of certain specified goods- Includes the list of exempt goods supplies, Annexure to Rule 138(14), items classified as no supply under Schedule III, and specific schedules to Central Tax Rate notifications.
Cancellation Of GST E-Way Bill
When an E-way bill is not delivered to the specified location or is not delivered according to the details in the created E-way bill within 24 hours of issue, the bill is immediately revoked by the common portal.
The cancellation can be done automatically through a common portal or manually through a Facilitation Center by a commissioner's order. The cancellation may be completed by going into the common portal with the Facilitation Center's ID and password. The cancellation, however, is not allowed if the bill is confirmed in transit as required by Rule 138B.
Items Exempted Under GST E-Way Bill
The federal government has issued a list of specifics completely excluded from the GST's e-way bill provision. These products are deemed common-use items and are excluded from the GST scheme's requirement for electronic authorisation for transportation.
According to the goods and services tax, a permit, i.e. an E-way bill, is required to transport consignments with a value of more than Rs. 50,000 to prevent tax evasion. However, during a recent GST Council meeting on August 5, a list of 153 items was released that is entirely free from requiring any kind of e-way bill during shipment.
Some of the things on the list that are excluded from the e-way bill include:
- LPG
- Kerosene
- Jewellery
- Currency
- Live Bovine Animals
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Fresh milk
- Honey
- Seeds
- Cereals
- Flour
- Betel Leaves
- Raw Silk
- Khadi
- Earthen Pot
- Clay Lamps
- Pooja Samagri
- Hearing Aid
- Human Hair
- Frozen Semen
- Condoms
- Contraceptives
Advantages Of The E-way Bill
Minimum Documentation: Transportation of products necessitates a significant amount of documentation. Especially when the movement is intra-state or inter-state, with an e-way bill, you don't have to keep track of any paperwork since the e-way bill keeps track of everything. Furthermore, it is reachable by transporters. Once you receive the e-way bill, you will never need the paper documents again.
Cost Efficient: The projected expenditure will be reduced by the E-way bill. The use of an e-way bill would result in more accurate invoicing and, as a result, less unnecessary costs.
Time Efficient: Optimal utilisation of vehicle/resources due to faster cargo transportation.
Easy to Use: E-way invoices are very simple to comprehend and apply. Even merchants can self-download the e-way bill without much difficulty.
Easy Generation: E-way bills would be made efficiently and quickly, and producing them would not be a huge task. It will be made extraordinarily simple soon since the government is working meticulously.
Disadvantages Of The E-way Bill
Poor Internet Network: A bad online network or lack of accessibility in most regions might be serious.
Distinctive Assessment from the Various States: Most states’ e-way bill system is controversial. The great majority of states must implement their own e-way bill system, which may become a massive cluster in the future.
Errors in Creating E-way Bills: When it comes to e-way bills, the e-way bill gateway can generate problems.
Penalties For Non-Generation Of E-Way Bill
The penalties of failing to generate and carry the EWay bill might include both financial and non-financial costs to the taxpayer.
Monetary Penalty: The individual transporting the items should pay a penalty of Rs. 10,000 or an equal amount of tax is avoided if an E-Way bill is not generated (the greater two).
Seized or Detained: It is possible to confiscate or detain a vehicle transporting goods without an E-Way bill. The car will be released only after paying the penalty and tax assessed by the officer. There are a variety of scenarios that might arise as a result of this:
- If the owner desires to pay the penalty, he must pay the full amount of the tax due.
- If you don't, you'll be fined 50% of the worth of your items.
Latest Developments In E-Way Bills
- Factor Authentication is mandatory for taxpayers with AATO Rs 20 Crore and above from 20th November 2023. Tax Payers should register for 2FA and also create sub-users so that EWB activities are managed without any problem.
- Returning non-filers will be unable to generate e-way bills beginning August 15.
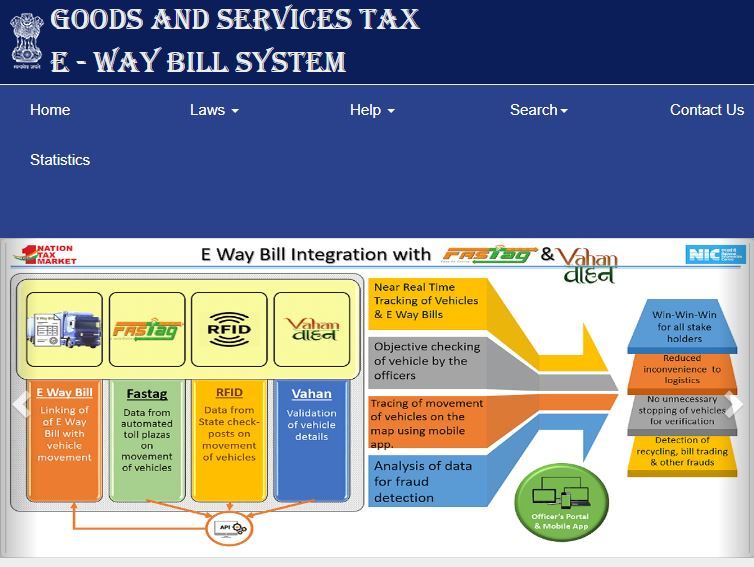
- By integrating the e-way bill (EWB) system with FasTag and RFID, GST officers now have real-time data on commercial vehicle traffic on roads. This action will aid in the continuous monitoring of such cars and detect GST evasion.
- Allowing e-way bills is only possible for intra-state gold transit, not inter-state.
- B2B and export invoices with the document type "TAX INVOICE" are ineligible for e-way bill production using the e-way bill site.
- B2C bills, import invoices, and other invoices do not require an IRN. For these invoices, direct e-way bills can be created.
- The computation of distance using the Seller's and Buyer's Postal Identification Numbers is one of the most significant modifications in the e-way bill. For distance calculations, the Distance Between Two PINs is employed.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Will the consignment value include the invoice value or the value of items if invoices are issued for both products and services?
Only products and not services are included in the consignment value. Furthermore, the HSN code is exclusively used to identify commodities.
2. What should be done if expired goods are transported?
In such circumstances, no bills are issued, but a delivery challan is issued. As a result, in conveying expired merchandise, delivery challans will be utilized to produce e-way invoices.
3. Who will produce EWB in the event of DTA sales from the SEZ/FTWZ?
The individual who started the movement must be a registered person, and that person must generate the e-way bill.
4. Can an e-way bill be generated and sent using a vehicle with a temporary number?
Yes, you can use a car with a temporary license plate.
5. Do empty transport containers require e-way bills?
E-way bills are not required for empty transport containers.
Conclusion
As a result, on the E-Way Bill System, an E-way bill aids in the seamless transportation and tracking of products. Even small firms may generate an E-Way Bill using simple techniques. Businesses should utilize it to comply with the law and facilitate the flow of goods.